Introduction:
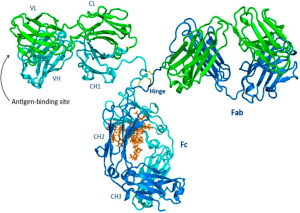
Antibodies, as pivotal components of the immune system, have been employed in various scientific and medical fields. The generation of antibodies, as a critical aspect of immunological responses, has garnered significant attention in biomedical research and clinical applications. The methodologies for producing antibodies can be broadly categorized into polyclonal and monoclonal approaches, each with distinct protocols and resultant antibody populations. This article delves into the methods of production, differences, advantages, and disadvantages of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, and explores their applications and prospects in the scientific research market.
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are a diverse mixture of antibodies produced by different B cell lineages within an immunized host, typically a rabbit or goat. The process begins with the administration of the target antigen, following which the host’s immune system generates a broad spectrum of antibodies recognizing multiple epitopes on the antigen. The antiserum, containing this heterogeneous antibody population, is then collected and may undergo further purification to obtain the desired antibody fraction.
The general procedure to produce polyclonal antibodies is as follows:
1 Antigen preparation
2 Adjuvant selection and preparation
3 Animal selection
4 Injection and ELISA titer testing
5 Blood serum extraction and antibody purification.
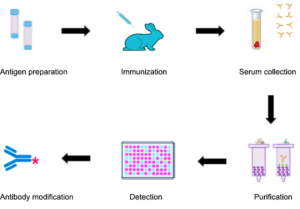
Fig1. Polyclonal Antibody Production Procedure
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are homogeneous antibodies that originate from a single B cell lineage, ensuring uniform specificity towards a particular epitope on the antigen. The quintessential method for mAbs production is hybridoma technology. In this technique, a mouse is immunized with the target antigen, and subsequent fusion of the isolated B cells with myeloma cells results in hybridoma cells. These hybridomas are then cultured, and the produced mAbs are harvested and purified, ensuring a consistent, high-specificity antibody population.
The general procedure to produce monoclonal antibodies is as follows:
1 Immunization of mice & isolation of splenocytes
2 Preparation of myeloma cells
3 Cell Fusion
4 Clone screening and picking
5 Functional characterization
6 Expansion and purification
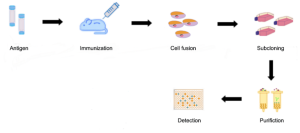
Fig2. Monoclonal Antibody Production Procedure
The following table shows the major differences between polyclonal and monoclonal:
| Feature |
Polyclonal Antibodies |
Monoclonal Antibodies |
| Source |
Multiple B-cell lineages |
Single B-cell lineage |
| Epitope Recognition |
Multiple epitopes |
Single epitope |
| Production Method |
Immunization of animals |
Hybridoma technology |
| Specificity |
Lower |
Higher |
| Production Time |
Shorter |
Longer |
| Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
| Batch Consistency |
Lower |
Higher |
| Cross Reactivity |
Higher |
Lower |
| Applications |
Diagnostics, antivenom |
Diagnostics, therapeutics, research |
| Advantages |
Broad reactivity, cost-effective |
High specificity, consistent |
| Disadvantages |
Batch variability, cross-reactivity |
Expensive, time-consuming |
No matter monoclonal antibodies or polyclonal antibodies are widely used as diagnostic tools and therapeutic applications:
Diagnostic Applications of Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs):
*High Specificity: mAbs are renowned for their high specificity to a single epitope, which is vital in diagnostic assays where precise antigen recognition is crucial.
*Use in ELISA and Immunohistochemistry: Their use in Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and immunohistochemistry ensures accurate diagnostic results, aiding in the detection and monitoring of diseases.
*Detection of Specific Strains: mAbs can also be engineered to detect specific strains or subtypes of pathogens, making them invaluable in infectious disease diagnostics.
Diagnostic Applications of Polyclonal Antibodies (pAbs):
*Broad Reactivity: pAbs have the ability to recognize multiple epitopes on an antigen, which is beneficial in diagnostics where a broader recognition spectrum is advantageous.
*Use in ELISA: Like mAbs, pAbs are also utilized in ELISA and other diagnostic assays, especially when detecting a range of antigenic variants is crucial.
Therapeutic Applications of Monoclonal Antibodies:
*Targeted Therapy: mAbs have revolutionized cancer therapy, autoimmune disease management, and other fields by providing targeted therapies. They can be engineered to bind specific cells or proteins, modulating their activity.
*Personalized Medicine: With the advent of personalized medicine, mAbs can be tailored to individual patient profiles, optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
*Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs): mAbs are also utilized as drug carriers in antibody-drug conjugates, delivering toxic agents specifically to tumor cells while sparing normal cells.
Therapeutic Applications of Polyclonal Antibodies:
*Antivenom Production: pAbs play a crucial role in antivenom production, where a broad spectrum of antibodies is required to neutralize various toxins present in venom.
*Infectious Diseases: They are also utilized in passive immunotherapy for infectious diseases, providing a broad-spectrum immune response.
The marketing trends for monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are reflective of the evolving healthcare landscape and advancements in biotechnology. Below are several notable trends and projections based on recent market analyses:
The global market for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is on a robust growth trajectory. The market was valued at around $210.06 billion in 2022 and is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.04% from 2023 to 2030[1]. Another report estimates the mAbs market to reach $463 billion by 2030 from $187 billion in 2022[2].
On the other hand, the polyclonal antibodies market is also growing, albeit at a slower pace compared to mAbs. The global polyclonal antibodies market is expected to grow from $1.27 billion in 2022 to $1.35 billion in 2023, with a CAGR of 6.3%[3]. The market is projected to reach around $1.44 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 5.2% from 2023 to 2029[4].
Production and Technological Advancements:
The market for antibody production is expanding in response to the growing demand for targeted therapies. The antibody production market size accounted for $14.3 billion in 2022 and is estimated to grow at 11.8% to reach $44 billion by 2032[5].
Biosimilars Driving Cost Efficiency:
The advent of biosimilar monoclonal antibodies is a significant trend driving market growth. Biosimilars aim to reduce healthcare costs and increase treatment accessibility by providing cost-effective alternatives to original biologic drugs. A biosimilar monoclonal antibody costs 20%-25% less than the originator biologic drug, making treatment more affordable and accessible6.
Strategic Initiatives by Companies:
Top companies in the monoclonal antibody market are engaging in strategic acquisitions, collaborations, and partnership agreements to broaden their product portfolios and geographical reach. For instance, in March 2022, Sanofi S.A. collaborated with Seagen Inc. to design, develop, and market antibody-drug conjugates for cancer treatment using exclusive monoclonal antibody and antibody-drug conjugate technologies[6].
Alternative Treatment Methods:
The rise in alternative treatment methods and natural remedies is expected to challenge the revenues of the monoclonal antibody drugs market. Treatments in homeopathy, Ayurveda, yoga, acupuncture, and sujok therapy are gaining popularity, posing competition to traditional biologic drugs[6].
Regional Market Dynamics:
Regional market dynamics, including new regulatory guidelines like the ‘Guidelines on Similar Biologics’ in India, are expected to boost the biosimilar industry, subsequently impacting the monoclonal antibodies market[6].
These trends underscore the dynamic nature of the antibodies market, influenced by technological advancements, strategic industry initiatives, and evolving healthcare paradigms. The promising growth projections for both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies markets signify their critical role in the future of diagnostics, therapeutics, and biomedical research.
For specific details, please consult the official website of KMD Bioscience:https://www.kmdbioscience.com/
Kindly note ; This article serves as a reference material for enthusiasts in scientific research. It does not substitute for professional knowledge or hands-on experimental procedures which require more detailed and professional information. In case of any content infringement, kindly reach out to the author for immediate deletion of the contentious material.
Reference link:
1 https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/monoclonal-antibodies-market
2 https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2023/10/16/2761090/0/en/Monoclonal-Antibodies-Market-Size-Projections-Exhibit-a-CAGR-of-12-0-Likely-to-Attain-a-Value-of-USD-463-0-Billion-by-2030.html#:~:text=Newark%2C%20Oct,The%20prevalence%20of
3 https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2023/08/24/2731329/0/en/Polyclonal-Antibodies-Global-Market-Report-2023.html#:~:text=The%20global%20polyclonal%20antibodies%20market,Ukraine%20war%20disrupted
4 https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2023/05/16/2669872/0/en/Polyclonal-Antibodies-Market-is-to-reach-USD-1-44-Billion-by-2029-at-a-growth-rate-of-5-2-percent-over-the-forecast-period.html#:~:text=The%20Polyclonal%20Antibodies%20Market%20size,from%202023%20to%202029
5 https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/antibody-production-market#:~:text=Antibody%20Production%20Market%20size%20accounted,diseases%2C%20such%20as%20cancer
6 https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2023/03/07/2622442/28124/en/Global-Monoclonal-Antibodies-MAbS-Market-Report-2023-Major-Players-Include-Merck-AbbVie-Amgen-GlaxoSmithKline-Norvatis-and-Pfizer.html